Economy
The Zambian economy grew by 3.5% in 2023 to reach US$ 27 billion. Its key economic sectors are mining and quarrying (mostly copper), agriculture, and services. In 2024, the IMF projects a real GDP growth rate of 2.3%.
Amid ongoing debt restructuring efforts and challenges from severe drought, Zambia’s economy is showing resilience. From 2021 to 2023, the nation’s real GDP experienced an average growth rate of 4.2%, though growth slowed significantly in 2024 due to climate-related issues.
The World Bank explains that recent economic performance has been driven by expansions in the mining, transport, information and communications, finance and insurance sectors, despite setbacks in agriculture and energy production due to drought conditions.
Introduction to the Economy of Zambia
Known for its rich mineral resources, particularly copper, Zambia’s economic landscape is influenced by various sectors including mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
Historical Context
Zambia’s economy has evolved from a predominantly state-controlled system in the early post-independence years to a more market-oriented framework. The liberalization policies of the 1990s, aimed at encouraging private investment and enhancing economic efficiency, marked a significant shift. Despite these efforts, Zambia has faced economic volatility, largely due to its dependence on copper exports.
Zambia’s Macro Economic Performances in 2021 and 2022
Zambia’s Macro Economic Performances in 2023 and 2024
According to the Bank of Zambia, Zambia’s real GDP growth slowed to 3.0% in 2023 and further to 1.2% in 2024.
The economic growth in 2023 was primarily driven by key sectors such as information and communication, education, and financial and insurance activities, shifting focus away from the traditionally prioritized sectors of mining, agriculture, and manufacturing.
The African Development Bank (AfDB) explains that the economic slowdown in 2024 was primarily due to contractions in the agriculture and energy sectors, despite some gains in mining and services.
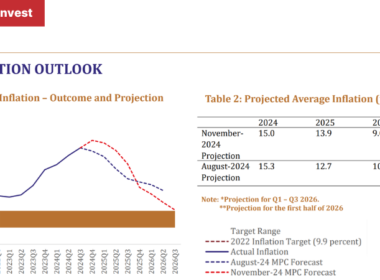
Inflation increased to an average of 14.6% in the second quarter of 2024 from 13.5% in the first quarter, driven by the persistent depreciation of the Kwacha against major currencies and rising food and energy prices.
Zambia Economic Statistics 2015-2024
| Description | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Population (millions) | 15.5 | 15.9 | 16.4 | 16.9 | 17.4 | 17.9 | 18.4 | 19.6 | 20.1 | 20.7 |
| ** Nominal GDP at Market Prices (US$ million) | 21,249.3 | 21,089.8 | 25,711.1 | 27,298.4 | 23,271.4 | 19,384.0 | 21,160.6 | 29,850.7 | 27,000.0 | 29,850.7 |
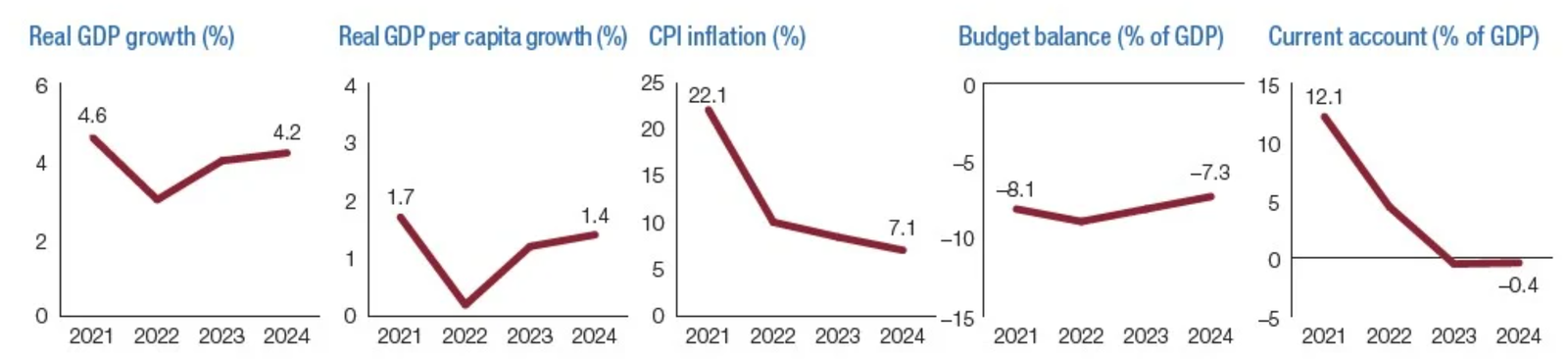
| Real GDP Growth rate, % | 2.9 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 1.4 | -3.0 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 3.0 | 1.2 |
| GDP per Capita, US$ | 1,377.3 | 1,331.0 | 1,567.3 | 1,616.5 | 1,596.2 | 1,083.8 | 1,157.5 | 1,522.2 | 1,342.3 | 1,441.6 |
| Inflation Rate (average), % | 10.0 | 18.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 15.7 | 22.1 | 11.1 | 9.9 | 14.6 |
| Foreign Exchange Reserves (Months of Import Cover) | 4.5 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 5.0 |
Source: Bank of Zambia, World Bank, IMF.
Economic Structure
The Zambian economy is characterized by its reliance on the mining sector, which contributes significantly to GDP and export revenues. However, the agriculture, manufacturing, and services sectors are also vital components of the economic structure, providing employment and contributing to overall economic growth.
Zambia Key Economic Indicators
Zambia Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
As of the latest data available for 2024, Zambia’s GDP stands at approximately $29.8 billion, reflecting a modest growth rate of 1.2% per annum. This growth has been significantly impacted by drought conditions affecting agriculture and energy production, though partially offset by gains in mining and services sectors.
Zambia Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation in Zambia has been a persistent issue, influenced by both domestic and international factors. The annual inflation rate in 2024 averaged 14.6%, up from single-digit figures in 2023, owing to currency depreciation and rising food and energy costs. The Bank of Zambia has maintained relatively high interest rates to control inflation, with the policy rate at 9.5% as of mid-2024.
Employment and Unemployment
The unemployment rate in Zambia is estimated to be around 13%, with higher rates among the youth. Employment is largely concentrated in the informal sector, which accounts for approximately 80% of the labor force.
Forign Exchange
In 2024, the Zambian Kwacha has shown remarkable resilience and strength against major currencies, particularly the US Dollar. After reaching a record low of 27.23 ZMW per USD in January, the Kwacha has steadily appreciated, trading around 22.40 ZMW per USD by October. This represents a significant 13.8% year-to-date appreciation, making it one of Africa’s best-performing currencies in 2024.
The Kwacha’s strong performance is attributed to aggressive monetary policies implemented by the Bank of Zambia, including increased interest rates and higher reserve ratios for commercial banks. Reduced import demand and improving foreign exchange reserves have also contributed to this positive trend.
Despite this overall strengthening, the Kwacha has experienced some volatility, with slight fluctuations observed throughout the year. Looking ahead, economists anticipate the exchange rate to stabilize around 21-22 ZMW per USD, though this outlook depends on continued foreign currency inflows and successful implementation of economic reforms.
This current strength marks a significant turnaround from the Kwacha’s historical trend of depreciation against major currencies over the past decade, particularly the sharp weakening observed between 2015 and 2020. The sustainability of this positive performance will largely hinge on Zambia’s ability to attract foreign investment, resolve debt issues, and maintain robust copper production and exports.
Sectoral Analysis
Zambia Mining Sector
The mining sector remains the cornerstone of Zambia’s economy, contributing over 70% of export earnings. Copper is the most significant mineral, with Zambia being one of the largest producers globally. Recent investments in mining infrastructure and technology have boosted production, but the sector faces challenges such as fluctuating global commodity prices and regulatory uncertainties.
Zambia Agriculture Sector
Agriculture employs about 60% of the workforce and contributes 19% to GDP. Major crops include maize, tobacco, and cotton. The sector’s growth has been significantly impacted by drought conditions in 2024, highlighting the need for climate-resilient agricultural practices.
Zambia Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing in Zambia is diverse, encompassing food processing, textiles, and chemicals. It accounts for about 8% of GDP. The sector is poised for growth with investments in value addition and industrialization strategies, though it has faced challenges due to energy shortages.
Zambia Services Sector
The services sector, particularly finance, tourism, and telecommunications, is increasingly significant, contributing approximately 50% to GDP. Growth in this sector has shown resilience even in the face of economic challenges, supported by urbanization and technological advancements.
Zambia Trade (Exports and Imports)
Zambia’s export portfolio is dominated by copper, followed by cobalt, tobacco, and horticultural products. Major trading partners include China, Switzerland, and South Africa. Imports primarily consist of machinery, transportation equipment, and fuel.
Zambia Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Zambia has experienced fluctuating levels of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in recent years. FDI inflows rose to $116 million in 2022, recovering from a negative inflow of $352 million in 2021. However, this was still lower than the 2018-2020 average of $504.3 million. In 2023, FDI inflows declined to $90 million.
As of 2022, the total stock of FDI in Zambia was estimated at $15.2 billion, representing about 53.5% of the country’s GDP. FDI remains dominated by large mining investments from countries like Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, China, and the United States.
The Zambian government has introduced new initiatives to attract investment. In April 2024, the Demand Stimulation Incentive was launched to attract investments in mini-grids. Additionally, the Zambia Development Agency unveiled a strategic plan for 2022-2026 aiming to attract $36 billion in FDI and Local Direct Investment.
Mining continues to be a major sector for FDI, particularly copper mining. Infrastructure projects, including road networks, railways, and power plants, are attracting significant foreign investment.
Government Policies and Economic Reforms
Fiscal Policy
The Zambian government has focused on fiscal consolidation to address the budget deficit and public debt, which stands at around 120% of GDP. Measures include expenditure cuts, improved tax collection mechanisms, and ongoing debt restructuring efforts.
Monetary Policy
The Bank of Zambia’s monetary policy aims to stabilize inflation and maintain exchange rate stability. Recent policies have included tightening the money supply and maintaining high-interest rates to combat inflationary pressures.
Challenges Facing Zambia’s Economy
Debt Burden
Zambia’s high public debt remains a major economic challenge, limiting fiscal space and increasing vulnerability to external shocks. Debt restructuring and negotiations with international creditors are ongoing, with progress made in 2024 including the exchange of Eurobonds for new notes.
Climate Vulnerability
The severe drought experienced in 2024 has highlighted Zambia’s vulnerability to climate shocks, particularly in the agriculture and energy sectors. This underscores the need for investments in climate-resilient infrastructure and diversification of energy sources.
Infrastructure Deficits
Infrastructure deficits, particularly in transport and energy, continue to hamper economic growth. Investments in road networks, railways, and power generation are critical for sustainable development and economic diversification.
Zambia’s Economy Future Outlook
Zambia’s economic prospects remain cautiously optimistic, with potential for recovery and growth driven by ongoing reforms, debt restructuring efforts, and investments in key sectors. The IMF projects real GDP growth to rebound to 4.4% in 2025 and 4.7% in 2026, assuming increased mining production, effective implementation of reforms, restoration of debt sustainability, and normalization of rainfall patterns.
Key factors for future growth include:
- Continued progress on debt restructuring to improve investor confidence and fiscal stability
- Diversification of the economy beyond copper mining
- Investments in climate-resilient agriculture and energy infrastructure
- Improvements in fiscal governance and revenue mobilization
- Ongoing support from international partners and implementation of economic reforms
While challenges remain, particularly in addressing climate vulnerabilities and maintaining macroeconomic stability, Zambia’s commitment to economic reforms and the support of international partners provide a foundation for future growth and development.
Last Updated: October 26, 2024